Selection Sort Algorithm Explained!
Selection Sort Algorithm with Java Program
In the previous article, I explained how the Bubble Sort algorithm works. Please have look at the Bubble Sort algorithm first before reading this article as it will be easier for you to learn the Selection Sort algorithm having Bubble Sort in mind. So, let's begin with this article now!
Introduction
As we know, sorting is a process of arranging a list of items in an order, so that the items in the list are arranged either in ascending order or descending order. To sort a list, we will see how selection sort works in this article.
In the Selection sort algorithm, we use an approach to find the maximum or the minimum element in an array at each step and perform the swap with the last or first indexed element respectively (basically to its correct position), it helps us to sort that particular element in the array. At each step, we also reduce the search space to find the max or min element in the array and to swap the elements as the array starts to sort after each step. One use case for selection sort is that it performs well with small lists/arrays. So, without further ado, let's jump right into the flow to learn Selection Sort.
Scope
- Algorithm for Selection Sort
- Java Program for Selection Sort
- Space and Time complexity analysis
Algorithm for Selection Sort (Ascending Order)
First, let's see, what are we going to do in the selection sort algorithm, and then we will jump right onto the how we gonna do it part. So, let's begin!
What are we doing?
Let's suppose, we have been given an array [4, 3, 5, 2, 1] (sorted array should be [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]). We are going to perform swaps step-by-step (swap simply means to exchange the array elements):
Step 0: First, we are finding the maximum element's index and then performing the swap with the last index. Here, 5 is the max element with index 2, so we swap it with the value 1 having index 4 (the last index in the current array search space).
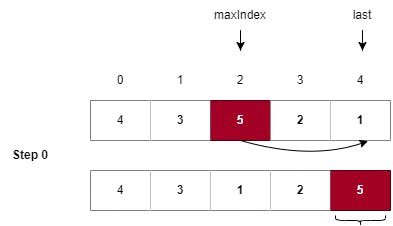
Note: As we have completed Step 0, we can see that the maximum element in the array has been shifted to the last index of the array, i.e., the last index of the array is now sorted. This also means that we will reduce our search space for the max element by 1 from the end.
Step 1: Now, we are finding the maximum element's index in the reduced array space and then performing the swap with the current array space's last index. Here, 4 is the max element with index 0, so we swap it with the value 2 having index 3 (the last index in the current array search space).
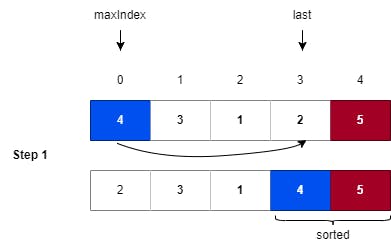
Note: As we have completed Step 1, we will reduce our search space for the max element by 1 from the end.
Step 2: Again, we are finding the maximum element's index and performing the swap with the current array space's last index. Here, 3 is the max element with index 1, so we swap it with the value 1 having index 2 (the last index in the current array search space).
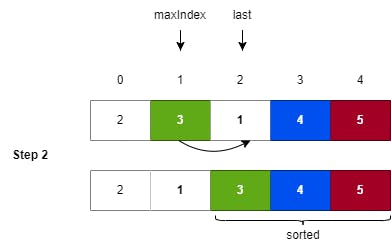
Note: As we have completed Step 2, we will reduce our search space for the max element by 1 from the end.
Step 3: Again, we are finding the maximum element's index and performing the swap with the current array space's last index. Here, 2 is the max element with index 0, so we swap it with the value 1 having index 1 (the last index in the current array search space).
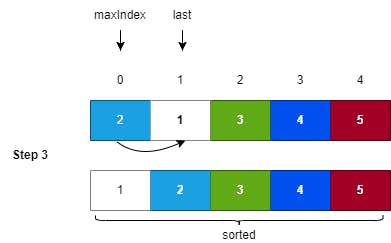
Note: As we have completed Step 3, our array is now sorted completely. We don't have to check for the remaining one element (1) in the array as when the (n-1) elements of the array become sorted the last element is automatically sorted. (n: size of the array)
Similar to the above approach, we can sort the array by finding the minimum element at each step and swapping it with the first index of our search space array. See the below image to understand the selection sort mechanism with a minimum element approach.
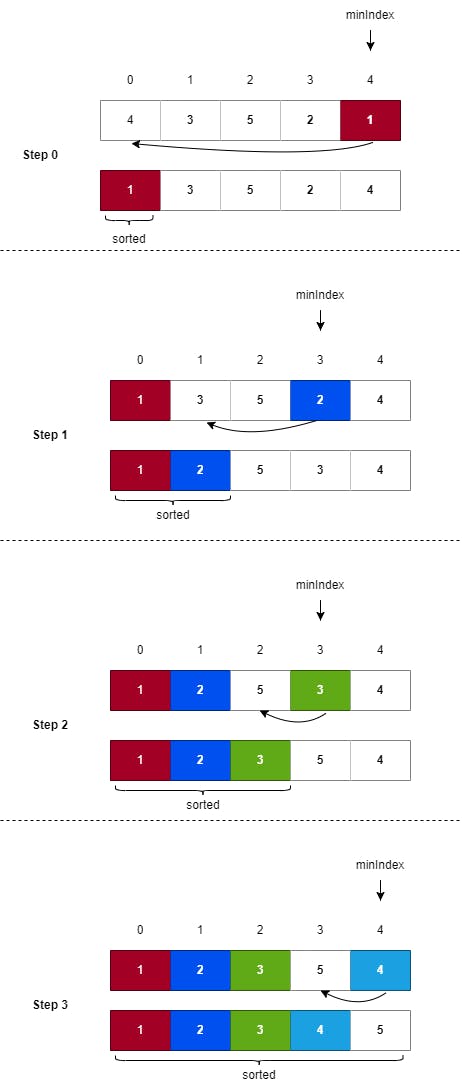
Now, let's see how we can convert the above approach into an algorithm that will help us to program a solution for Selection Sorting.
How we are doing it? (Flow Algorithm for Selection Sort (Maximum element))
- First, we have to initialize an array of elements or take user input for the array elements in the main method.
- Then, we call the
selectionSort(arr)method (passing thearras a parameter in the function), which will shift the control to theselectionSort()method. - We run a for loop in the
selectionSort()method, and iteratorirepresent our steps count, such that0 ≤ i < n-1, where n is the length of the array. - We declare a
last = n - i - 1variable that will be used to reduce our search space for finding the maximum element and swapping it with its correct position. - We call the
max(arr, 0, last)function, which will give us the maximum element's index in the current search space, i.e.,start = 0andend = last. - Now, we just swap the maximum element's index value with the last element.
- We repeat the above two steps at each pass until our
i < n-1. - In the end, the control comes back to the
main()function, and we print the sorted array using theArrays.toString()method in Java.
Java Program for Selection Sort
Static Code for Selection Sort Java (GitHub)
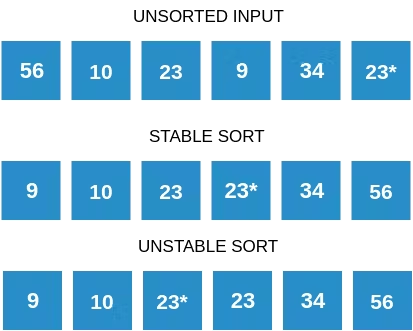
Note: Selection sort is not a stable sorting algorithm.
Space and Time Complexity Analysis for Selection Sort
Recommended visiting Asymptotic Notations and Guidelines for Asymptotic Notations.
Time Complexity for Selection Sort
Average Case: As we are running nested loops (one for the steps count, and one for finding the maximum element's index) for the length of the array, the average case time complexity also comes out to be O(N2).
- One loop to for the steps count = O(N)
- Another loop to find the maximum element's index = O(N)
Overall complexity = O(N) * O(N) = O(N*N) = O(N2)
Best Case and Worst Case complexities also come out to be O(N2) as we are running the loops no matter whether it is sorted or not.
Space Complexity for Selection sort
Space complexity for the selection sort algorithm is O(1), as it is an in-place sorting algorithm and doesn't take up any extra space to sort the array.
Outro
Thank you for reading this article, I hope that you were able to understand how selection sort algorithms work. Try to play around with the code, put debug pointers while running the program, use different input arrays, and use pen and paper to see how the algorithm works. Afterward, please leave a like and share it with your friends and family!
Happy Coding! :))
Reference: Kunal Kushwaha

